By Mike Gibson and Ivor Catt, June 1986
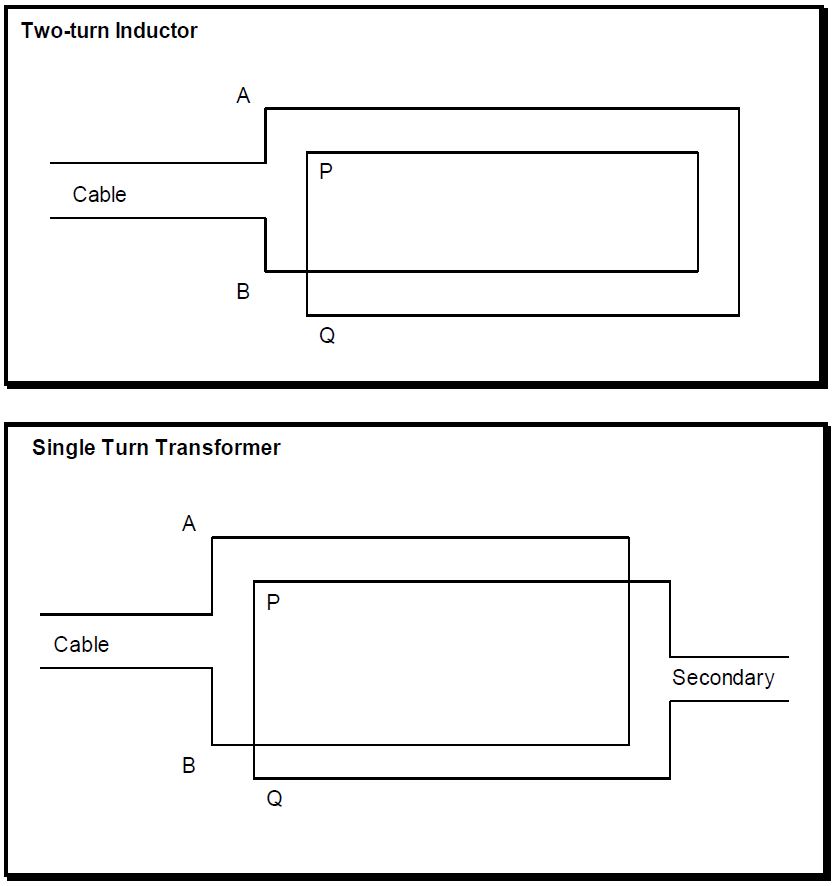
Here is a description of the symbols used in the derivations:
\(V_{F C}\) voltage on cable moving towards the inductor
\(V_{R C}\) voltage on cable moving away from the inductor
\(Z_C\) characteristic impedance of the cable
\(V_{F E}\) voltage traveling in the forward direction in the even mode
\(V_{F O}\) voltage traveling in the forward direction in the odd mode
\(V_{R E}\) voltage traveling in the reverse direction in the even mode
\(V_{R O}\) voltage traveling in the reverse direction in the odd mode
\(Z_E\) characteristic impedance of even mode
\(Z_O\) characteristic impedance of odd mode
\(V_{F S}\) secondary voltage moving away from the transformer
\(V_{R S}\) secondary voltage moving towards the transformer
Going from the cable to the inductor, the following basic equations hold,
$$\begin{equation}
\begin{aligned}
&1) \qquad V_{F C}+V_{R C}=V_{F E}+V_{F O}=V_{A B} \\
&2) \qquad I_{F C}+I_{R C}=I_{F E}+I_{F O}=I_{A B} \\
&3) \qquad V_{F E}-V_{F O}=V_{P Q}=0
\end{aligned}
\end{equation}$$
Transforming (2) into voltages gives,
$$4) \qquad \frac{V_{F C}}{Z_C}-\frac{V_{R C}}{Z_C}=\frac{V_{F E}}{Z_E}+\frac{V_{F O}}{Z_O}$$
Multiplying through by ZC and defining new terms for the resulting ratios yields,
$$5) \qquad V_{F C}-V_{R C}=r_E V_{F E}+r_O V_{F O}$$
$$6) \qquad \boxed{
\begin{aligned}
&r_E=\frac{Z_C}{Z_E}\
&r_O=\frac{Z_C}{Z_O}
\end{aligned}}
$$
From (1),
$$7) \qquad V_{R C}=V_{F E}+V_{F O}-V_{F C}$$
Substituting (7) into (5) and gathering terms,
$$7) \qquad V_{F C}-V_{F E}-V_{F O}+V_{F C}=r_EV_{F E}+r_OV_{F O}$$